Cold Chain Logistics: A Comprehensive Overview
What is Cold Chain Technology?
The term “cold chain” refers to a specialized supply chain system that ensures perishable goods remain in a required low-temperature environment throughout their journey—from sourcing or harvesting, through processing, storage, transportation, distribution, and retail, until they reach consumers. This process guarantees food safety, minimizes loss, and prevents contamination.
Definitions of Cold Chain Across Different Regions
Cold chain has different interpretations worldwide:
- China: A logistics network designed to maintain low temperatures throughout the entire production-to-consumption process to preserve product quality.
- United States: A continuous process from farm to table that maintains the correct temperature to inhibit bacterial growth.
- European Union: A temperature-controlled process covering raw material supply, production, processing, storage, and final consumption.
- Japan: A low-temperature distribution system that keeps fresh food and raw materials in optimal condition using refrigeration, freezing, and low-temperature storage techniques.
Despite regional variations in definition, all emphasize the importance of “cold” (low temperature) and “chain” (from production to consumption), which are fundamental to cold chain logistics.
Cold Chain Logistics Process
Cold chain logistics refers to a systematic approach where perishable goods, including refrigerated and frozen items, remain within a specified temperature range from production to consumption. This system has evolved with advancements in refrigeration technology and logistics management.
The “3T Principle” of Cold Chain
Cold chain logistics must adhere to the 3T Principle, which states that the final quality of a product depends on:
- Time – Duration of storage and transportation.
- Temperature – Maintained temperature during handling.
- Tolerance – The product’s ability to withstand storage conditions.
This principle highlights the relationship between storage duration and temperature control, ensuring that perishable products retain their quality while reducing irreversible degradation during distribution.
Applications of Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics applies to various industries, including:
- Primary agricultural products: Meat, seafood, poultry, eggs, vegetables, fruits, frozen foods, dairy products, and beverages.
- Processed foods: Frozen and packaged foods, ice cream, dairy items, and quick-frozen meals.
- Specialized products: Flowers, plants, pharmaceuticals, tea, and chemical materials.
Food Cold Chain
The food cold chain (or refrigeration chain) ensures that perishable food products remain at specified low temperatures throughout their journey, reducing spoilage and preserving safety. It integrates refrigeration technology into logistics, requiring comprehensive coordination of production, transportation, sales, and economic factors.
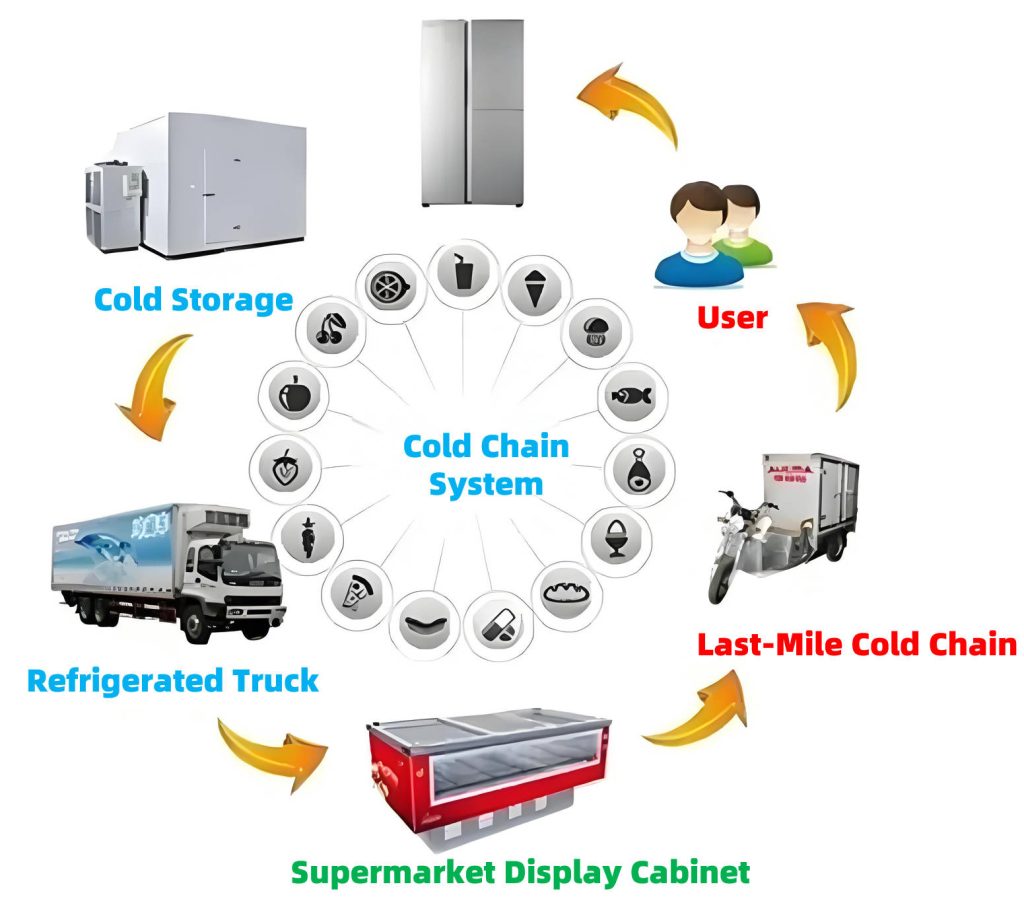
The food cold chain consists of four major components:
- Frozen Processing: Includes cooling and freezing meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products, as well as pre-cooling and processing of fruits and vegetables. Key equipment includes cooling and freezing units and quick-freezing devices.
- Frozen Storage: Ensures optimal conditions for long-term storage of perishable goods, including air-conditioned storage for fruits and vegetables. Facilities include cold storage warehouses, refrigerated cabinets, and household refrigerators.
- Refrigerated Transport and Distribution: Covers transportation via refrigerated trucks, rail cars, ships, and containers to maintain low temperatures. Temperature stability is crucial, particularly for long-distance shipping.
- Frozen Sales: Involves refrigerated storage and retail distribution. Supermarkets, wholesale distributors, and retailers play key roles in ensuring continuous cold storage for food products. Refrigerated display cases and storage units are essential components.
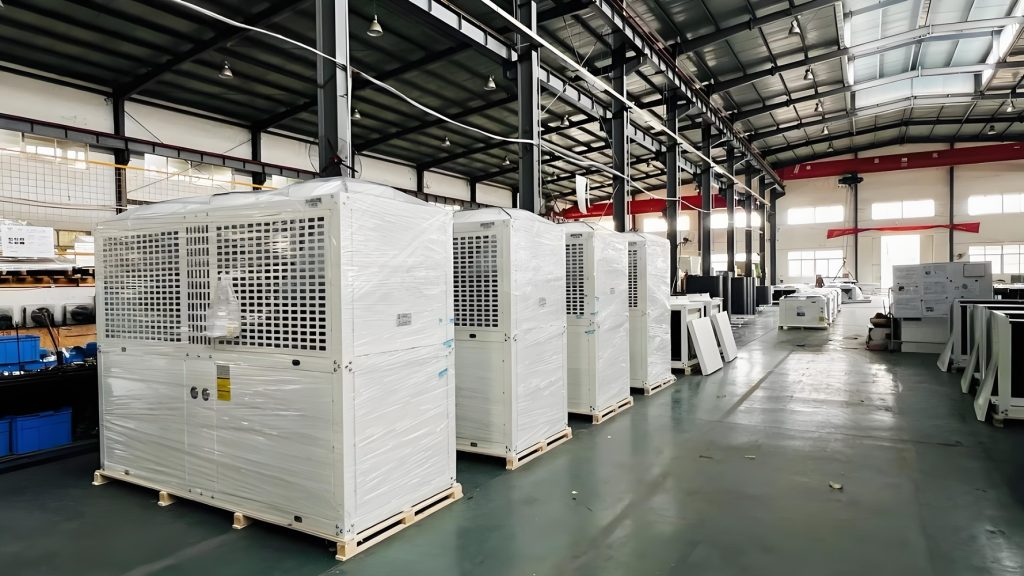
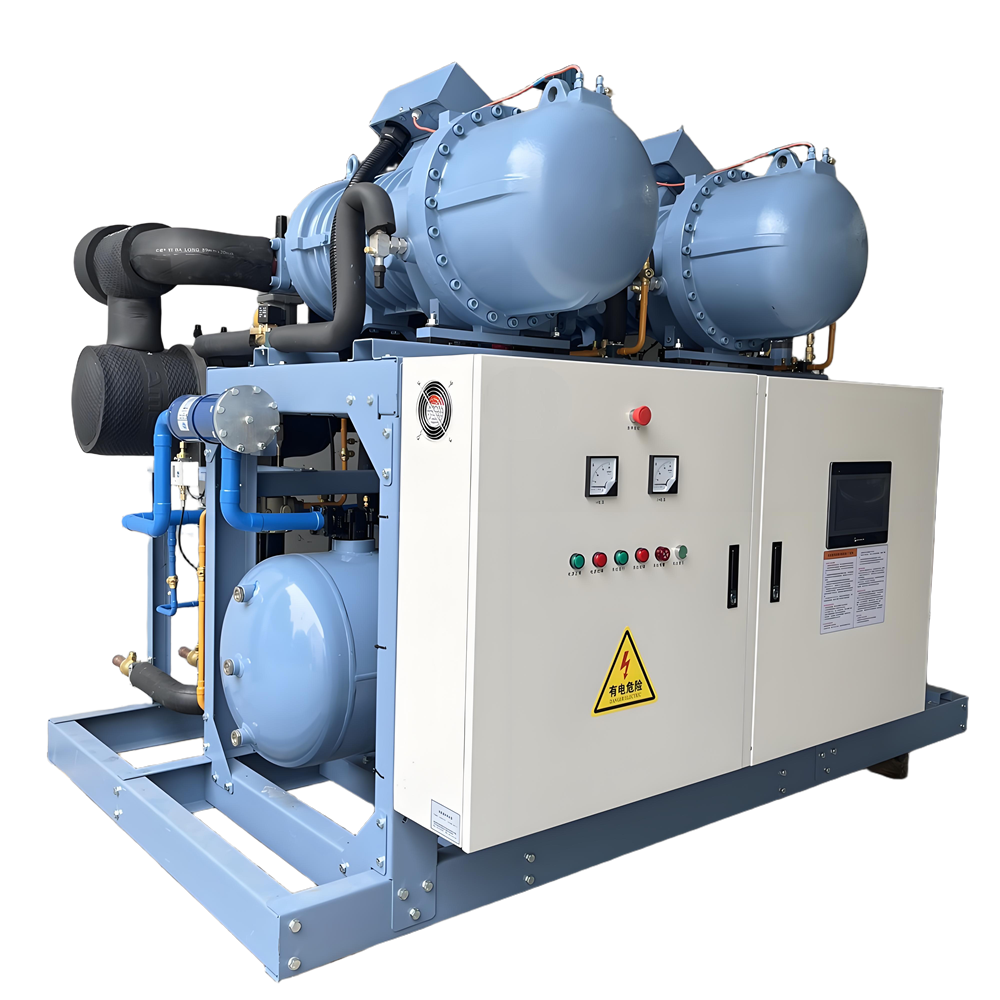
Cold Chain Equipment
Cold chain equipment plays a vital role in maintaining product quality by providing necessary temperature control. Common cold chain equipment includes:
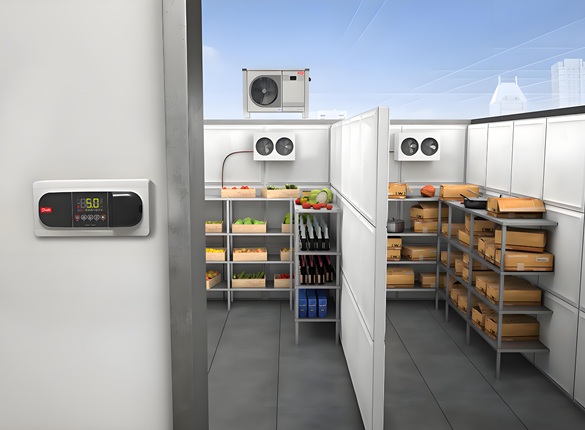



- Cold storage warehouses: Low-temperature storage facilities.
- Refrigerated display cases: Used in retail and supermarkets.
- Cold storage trucks: Vehicles designed for refrigerated transportation.
- Cold storage containers: Insulated containers for long-distance shipping.
- Vaccine transport vehicles: Specialized for medical cold chain logistics.
- Backup ice packs: Auxiliary cooling materials.
Conclusion
Cold chain logistics is an indispensable part of modern supply chain management, ensuring the integrity of perishable goods from production to consumption. With increasing demand for food safety, pharmaceutical transportation, and temperature-sensitive goods, the development of cold chain technology and logistics systems will continue to be a key focus for global industries.





